Whether you’re a high school student checking your test score or a college teacher grading assignments, knowing how to calculate grades accurately is essential for academic performance and success. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about calculating grades, from basic test scores to complex weighted averages used in college applications.
Understanding Grade Calculations: The Basics
Before diving into formulas and methods, let’s cover the fundamental concepts that make up any grade calculation. Understanding the grading system used by your institution is crucial for academic success.
What Are Grades?
Grades are numerical or letter-based representations of academic performance. In the United States, the most common grading system uses letter grades (A, B, C, D, F) alongside percentage grades. Understanding how these two systems relate is the first step in calculating grades effectively.
A good grade not only reflects your academic performance but also impacts college admissions and future opportunities. That’s why knowing how to calculate grades accurately matters so much in student life.
The Standard Grading Scale
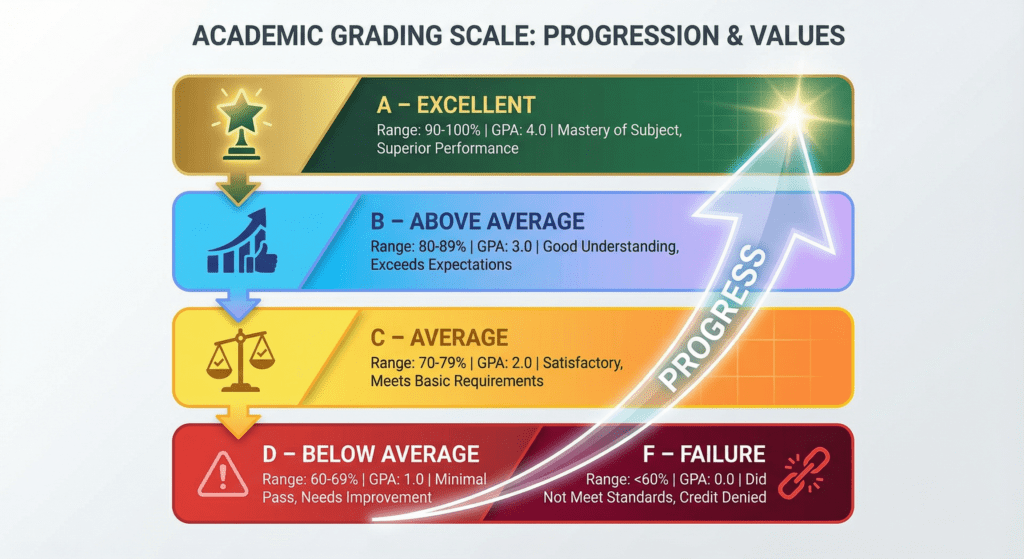
Most schools and colleges in the US follow a standard grading scale that converts percentage scores into letter grade values:
- A (90-100%): Excellent performance
- B (80-89%): Above average work
- C (70-79%): Average/satisfactory work
- D (60-69%): Below average but passing
- F (Below 60%): Failing grade
Many institutions also use plus/minus grades (A+, A, A-, B+, etc.) to provide more detailed feedback on student performance. This grading schema helps both students and teachers understand exactly where performance stands.
How to Calculate Test Grades
The most straightforward grade calculation is for tests, quizzes, and assignments. Here’s the simple formula every student should know:
Test Grade = (Points Earned ÷ Total Points Possible) × 100
This basic formula converts your point value into a percentage score that determines your letter grade.
Test Grade = (Points Earned ÷ Total Points Possible) × 100
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s say you took a test with 40 questions and got 7 wrong:
- Calculate correct answers: 40 – 7 = 33 correct
- Divide by total questions: 33 ÷ 40 = 0.825
- Convert to percentage: 0.825 × 100 = 82.5%
- Round the decimal point: 82.5% rounds to 83%
- Find letter grade: 83% = B
You can verify this quickly using our free grade calculator which handles all the math instantly and helps you understand your class grade.
Handling Partial Credit
Not all questions are worth the same number of points. When dealing with partial credit or different point values:
- Add up all points earned across all questions
- Add up total possible points for the test
- Divide earned by possible and multiply by 100
Example: You earned 87 points out of 100 total points possible.
- Grade = (87 ÷ 100) × 100 = 87% (B+)
This calculation works whether you’re dealing with a simple quiz grade or a complex test with multiple sections worth different point values.
How to Calculate Weighted Grades
Many courses don’t weigh all assignments with equal weight. Your course grade often combines homework, quizzes, tests, and exams with different weight percentages. Understanding how to calculate a weighted average is crucial for knowing your overall grade.
The Weighted Average Formula
Weighted Grade = Σ(Grade × Weight) ÷ Σ(Weights)
Or in simpler terms: multiply each grade by its weight percentage, add them all up, then divide by the sum of all weights. This weighted average method gives more importance to higher-weight assignments.
Real-World Example
Let’s calculate a semester grade with these components using the weighted average method:
- Homework: 85% (worth 20% weight value)
- Quizzes: 90% (worth 10% weight value)
- Tests: 78% (worth 30% weight value)
- Final Exam: 92% (worth 40% weight value)
Calculation:
- Homework: 85 × 0.20 = 17
- Quizzes: 90 × 0.10 = 9
- Tests: 78 × 0.30 = 23.4
- Final: 92 × 0.40 = 36.8
Total Grade: 17 + 9 + 23.4 + 36.8 = 86.2% (B)
For complex grade calculations like this, try our weighted grade calculator to save time and avoid errors. It’s especially helpful when tracking multiple assignment grades throughout the semester.
How to Calculate What Grade You Need
One of the most common questions students ask is: “What do I need on my final to get an A?” Here’s how to figure it out using a final grade calculator approach.
The Required Grade Formula
Required Grade = (Target Grade – Current Weighted Score) ÷ Final Exam Weight
Step-by-Step Example
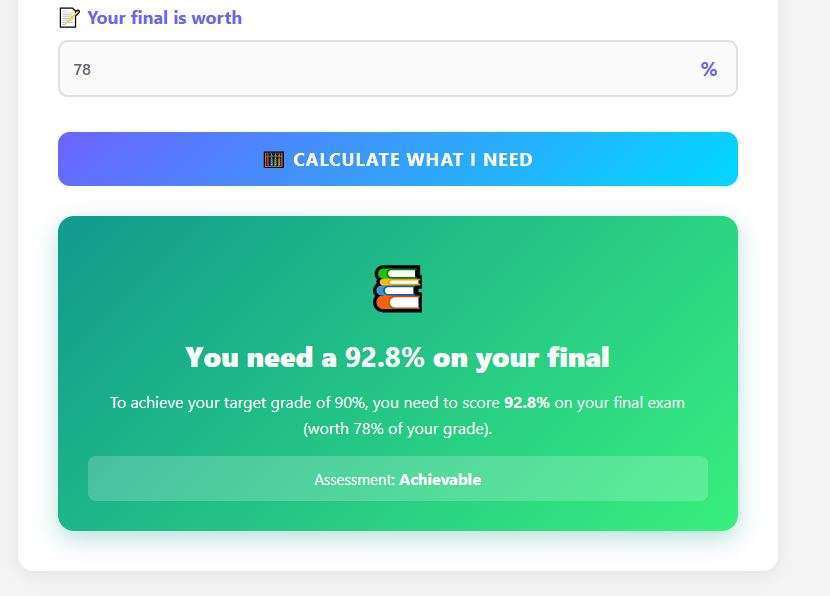
Suppose you want to achieve a 90% (A-) as your final score in your class:
- Your current grade is 85%
- The final exam grade is worth 40% of your total grade
- Completed work represents 60% of your grade
Calculation:
- Convert weights to decimals: 40% = 0.40, 60% = 0.60
- Calculate current weighted score: 85 × 0.60 = 51
- Calculate needed total score: 90 – 51 = 39
- Divide by final weight: 39 ÷ 0.40 = 97.5%
You’d need a 97.5% on your final exam grade to reach a 90% overall grade.
Check if your target is achievable with our final grade calculator which shows you exactly what percentage score you need and whether it’s realistic based on your current grade.
How to Calculate Cumulative Grades
Cumulative grades track your academic performance across an entire semester or multiple courses, measured as your Grade Point Average (GPA). This is especially important for college admissions and graduate students.
Understanding Grade Points
In the GPA point system, letter grades convert to grade points on a 4.0 scale:
- A = 4.0 grade points
- B = 3.0 grade points
- C = 2.0 grade points
- D = 1.0 grade points
- F = 0.0 grade points
These quality points are the foundation of calculating your overall GPA.
GPA Calculation Formula
GPA = Total Grade Points ÷ Total Credit Hours
Practical Example
Here’s a semester with 4 courses showing how to calculate your grade point average:
| Course | Letter Grade | Credits | Grade Points | Quality Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Math | B (3.0) | 4 | 3.0 | 12.0 |
| English | A (4.0) | 3 | 4.0 | 12.0 |
| History | B- (2.7) | 3 | 2.7 | 8.1 |
| Science | A- (3.7) | 4 | 3.7 | 14.8 |
Calculation:
- Total Quality Points: 12.0 + 12.0 + 8.1 + 14.8 = 46.9
- Total Credits: 4 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 14
- Overall GPA = 46.9 ÷ 14 = 3.35
Calculate your GPA across multiple semesters with our GPA calculator which handles both semester and cumulative GPAs. You can also use a spreadsheet to track your grades over time if you prefer manual tracking.
Common Grading Methods Explained
Different instructors use different grading options and approaches. Understanding these methods helps you calculate your grades accurately regardless of your teacher’s grading policy.
Points-Based Grading
In this point system, every assignment has a point value. Your course score equals the total points you earned divided by total points possible.
Example: You earned 450 out of 500 total points
- Grade = (450 ÷ 500) × 100 = 90% (A-)
Category-Based Grading
Assignment grades are grouped into categories (homework, tests, projects), each with its own different weight.
Example:
- Homework category: 85% grade average (20% weight)
- Test category: 88% grade average (50% weight)
- Project category: 92% grade average (30% weight)
Final Grade: (85 × 0.20) + (88 × 0.50) + (92 × 0.30) = 88.6% (B+)
Curved Grading
Some instructors “curve” grades by adjusting percentage scores based on class performance. There’s no universal curve formula, but common approaches include:
- Adding points: Everyone gets +5 points added to their raw score
- Scaling: The highest score becomes 100%, and all others scale proportionally
- Statistical: Scores are adjusted based on standard deviations from the average grade
Understanding your instructor’s grading policy helps you know exactly how your final grade will be calculated.
Grade Calculation Tips for Students
1. Track Your Grades Regularly
Don’t wait until the end of the semester to calculate your grade. Check your current grade after each major assignment to know where you stand. Many students find that using a spreadsheet or grades page helps them stay organized.
2. Understand Your Syllabus
Every course syllabus should explain:
- How assignment grades are weighted (weight percentage for each category)
- The grading scale used for letter grade conversions
- Whether extra credit is available
- If the lowest grade is dropped
- The grading policy for late work
Review your course syllabus at the beginning of each semester and refer back to it when calculating grades.
3. Focus on High-Weight Assignments
A poor quiz grade (worth 5%) affects your final grade much less than a poor test grade (worth 25%). Understanding the different weight of each assignment type helps you prioritize your study time and manage your student life better.
4. Use Grade Calculators
Manual grade calculations are prone to errors, especially when dealing with the number of grades across multiple categories. Using reliable tools like GradeCalcPro’s calculators ensures accuracy and saves valuable time. These tools also help with time management by showing you exactly where you stand.
5. Plan Ahead with Better Grades in Mind
If you’re aiming for a specific final grade, work backwards from your goal. Calculate what percentage grade you need on upcoming assignments and adjust your study strategies accordingly. This forward-thinking approach leads to better grades overall.
Grade Calculation Tips for Teachers
1. Be Transparent About Weights and the Grading Schema
Students perform better when they understand how grades are calculated. Clearly communicate assignment grades and weight values in your course syllabus at the start of the semester.
2. Use Consistent Scales
Stick to one grading scale throughout the course. Changing scales mid-semester creates confusion and seems unfair to students.
3. Consider Drop Policies
Many teachers drop the lowest quiz or homework grade. This accounts for one-off poor performances without penalizing students who demonstrate good grades overall. When calculating grades with a drop policy, remember to exclude the lowest score before computing the grade average.
4. Round Thoughtfully Using Proper Decimal Points
Establish clear rounding rules (e.g., 89.5% rounds to 90%). Apply them consistently to all students. Be careful with the decimal point – don’t round intermediate calculations, only the final percentage grade.
5. Provide Regular Grade Updates
Let students see their current grade throughout the semester via a grades page or learning management system. This helps them adjust their effort and reduces end-of-semester surprises. Regular feedback promotes better academic performance.
6. Document Your Grading Policy Clearly
Include detailed information in your syllabus about:
- The number of items in each category
- How you calculate the total grade
- Whether you use equal weight for all assignments or different weights
- Any special grading options like curves or extra credit
Understanding Different Grading Scales
The grading scale varies significantly by institution and even by instructor. Here are the most common variations you’ll encounter in high school and college:
Standard 10-Point Scale
This is the most common grading system in the US for both high school and college:
- A: 90-100%
- B: 80-89%
- C: 70-79%
- D: 60-69%
- F: Below 60%
7-Point Scale
Used by some schools, this stricter grading scale requires higher percentage scores:
- A: 93-100%
- B: 85-92%
- C: 77-84%
- D: 70-76%
- F: Below 70%
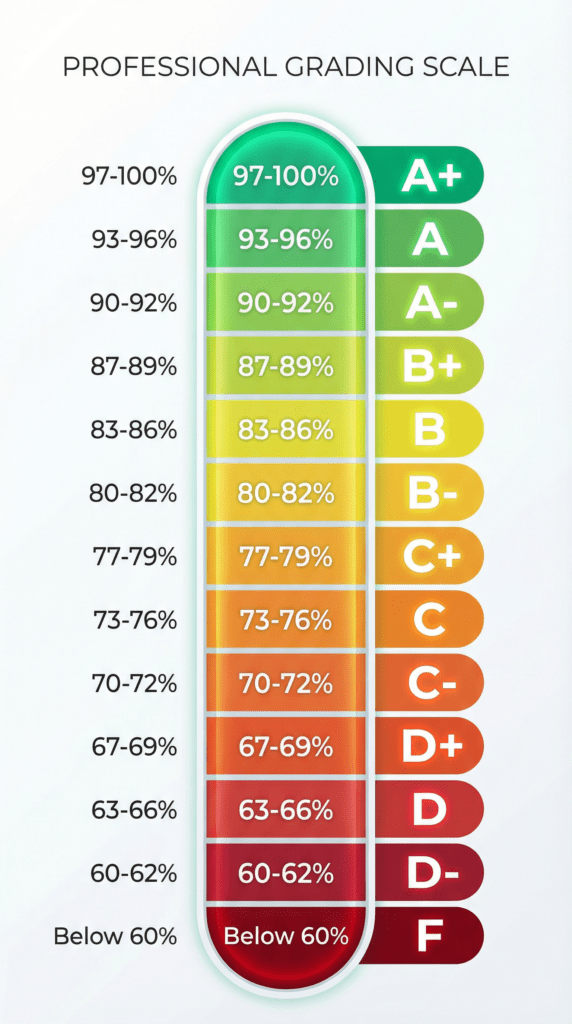
Plus/Minus System with Detailed Letter Grade Ranges
This provides more granular feedback on academic performance:
- A+: 97-100%
- A: 93-96%
- A-: 90-92%
- B+: 87-89%
- B: 83-86%
- B-: 80-82%
- (and so on…)
Always confirm which grading scale your instructor uses before calculating your grade. Check your course syllabus or ask during the first week of class.
Frequently Asked Questions About Calculating Grades
What’s a passing grade in high school and college?
In most US schools, a D (60%) is the minimum passing grade. However, many college programs require a C (70%) or higher for courses in your major. Graduate students often need a B average to remain in good standing. Always check your program’s specific requirements.
How do I calculate my grade if work is still incomplete?
Calculate your current grade using only completed assignments. Then use the weighted average formula to project different scenarios for remaining work. Our calculators can show you the number of points needed on future assignments to reach your target grade.
Can bonus points raise my grade above 100%?
Yes! Many grading systems allow extra credit or bonus points. A percentage grade above 100% is possible and can offset lower scores on other assignments. Some teachers include this as part of their grading policy.
What if my instructor doesn’t use standard weights?
Ask for clarification. Every course should have a syllabus explaining the grading schema. If the weight percentage for each category isn’t clear, email your instructor before calculating your grade.
How accurate are online grade calculators?
Reputable grade calculators like GradeCalcPro use standard mathematical formulas and are highly accurate for grade calculations. They eliminate human error in arithmetic and handle the decimal point correctly in all calculations.
Should I calculate my grade after every assignment?
While not necessary after every single new assignment, checking your grade average regularly (every 2-3 weeks) helps you stay on track and identify when you need to improve. This is good time management and helps maintain better academic performance.
How do I calculate a grade percentage from points?
Use this formula: (Points Earned ÷ Total Possible Points) × 100. For example, if you earned 85 out of 100 total points: (85 ÷ 100) × 100 = 85%. This gives you your percent grade.
What’s the difference between a course grade and a grade average?
A course grade is your final grade in a single class, calculated using all assignments and their weights. A grade average (like GPA) combines multiple course grades across different classes, weighted by credit hours.
Common Grade Calculation Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake #1: Forgetting to Weight Categories
Simply averaging all your assignment grades gives you an unweighted grade average. If assignments have different weight values, you must use the weighted average formula. This is one of the most common errors students make when calculating grades.
Wrong: (85 + 90 + 78 + 92) ÷ 4 = 86.25%
Right: Use the weighted formula with proper weight percentages
Mistake #2: Using the Wrong Grading Scale
Assuming your instructor uses a 90-80-70-60 grading scale when they actually use a 93-85-77-70 scale can lead to grade surprises. Always check your syllabus for the correct letter grade conversion chart.
Mistake #3: Not Accounting for Dropped Grades
If your course syllabus states “lowest quiz grade dropped,” don’t include it in your grade calculations. Many students forget this grading policy and calculate incorrectly.
Mistake #4: Rounding Too Early with Decimal Points
Round only at the final step of your calculation. Rounding intermediate calculations compounds errors and gives you an incorrect number.
Example:
- Wrong: 23.7 × 0.3 ≈ 7 (rounded during calculation)
- Right: 23.7 × 0.3 = 7.11 (round only at the end to get accurate grade percentage)
Mistake #5: Miscalculating Remaining Work
When calculating what you need on remaining assignments, make sure you account for their weight properly. Use a final grade calculator to verify your math.
Mistake #6: Forgetting About the Number of Items Per Category
When you have multiple items in a category (like 5 quizzes), calculate the average of those quiz grades first, then apply the category weight. Don’t apply the weight to each individual quiz.
Tools to Make Grade Calculation Easier
While understanding the math behind grade calculations is important, you don’t need to calculate everything by hand. Here are helpful tips and the best tools for calculating grades:
Online Calculators (Recommended)
- Grade Calculator: Calculate test scores and assignment grades instantly with our easy-to-use interface
- GPA Calculator: Track semester and cumulative GPA across multiple courses with accurate grade point conversions
- Final Grade Calculator: Find out what percentage score you need on finals to hit your target grade
- Weighted Grade Calculator: Handle complex weighted category calculations with different weight values
These tools save time and provide accurate grade calculations every time, whether you’re a high school student or working on your college application.
Spreadsheet Templates for Tracking
Create a simple spreadsheet with these column headers:
- Assignment name
- Number of points earned
- Total possible points
- Weight percentage
- Calculated grade
This gives you a running total grade as you complete work throughout the semester. Many students and graduate students find this helpful for long-term tracking.
Learning Management Systems
Most schools use platforms like Canvas, Blackboard, or Google Classroom that calculate grades automatically and provide a grades page. However, it’s still wise to verify the grade calculations yourself using the methods in this guide.
Average Calculator Tools
An average calculator can help you quickly find the mean of multiple test scores or assignment grades. This is particularly useful when calculating category averages before applying weights.
Final Thoughts on How to Calculate Grades
Calculating grades doesn’t have to be complicated. Whether you’re working with simple test scores or complex weighted averages, the key is understanding which formula to use and applying it correctly to get an accurate grade percentage.
For students, knowing how to calculate grades empowers you to:
- Set realistic academic performance goals
- Prioritize your study strategies and time management effectively
- Reduce stress by knowing exactly where you stand in each class
- Plan ahead for college admissions with accurate GPA tracking
- Make informed decisions about your student life and course load
For teachers, clear and consistent grade calculations:
- Build trust with students through transparent grading policies
- Reduce grade disputes and questions
- Help identify struggling students early in the semester
- Provide accurate academic performance feedback
- Support better teaching and assessment practices
Remember, while the formulas for calculating grades might seem complex at first, they’re just arithmetic once you break them down step by step. Whether you need to calculate a simple test grade, figure out your weighted average across multiple categories, or determine your overall GPA for college applications, the principles remain the same.
And when in doubt, using reliable tools like GradeCalcPro’s free calculators ensures accuracy every time. These calculators handle everything from basic percentage calculations to complex weighted averages, saving you time and reducing errors.
Ready to Calculate Your Grades?
Start tracking your academic performance today with our free grade calculation tools:
- Quick Test Scores: Use our grade calculator for instant percentage and letter grade results
- Semester Planning: Try our weighted grade calculator to track all your assignments
- GPA Tracking: Calculate your cumulative GPA with our GPA calculator
- Finals Preparation: Plan ahead with our final grade calculator
Take control of your academic success and start calculating your grades accurately today!