Your grade point average (GPA) is one of the most important numbers in your academic career. Whether you’re tracking your semester GPA, planning for college admissions, applying for financial aid, or preparing graduate school applications, knowing how to calculate GPA accurately is essential. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about calculating your GPA, from basic formulas to advanced scenarios.
Calculate Your GPA From Our GPA CALCULATOR
What Is a Grade Point Average (GPA)?
A grade point average is a numerical value that represents your overall academic performance across all coursework. In the United States, most schools use a GPA scale ranging from 0.0 to 4.0, where each letter grade corresponds to a specific point value. Your cumulative GPA combines all your course grades throughout your high school career or undergraduate degree program, while your semester GPA reflects only one term’s performance.
Understanding the GPA Scale
Before calculating GPA, you need to understand how letter grades convert to numerical values on the standard grading scale:
| Letter Grade | Grade Points | Numerical Value |
|---|---|---|
| A | 4.0 | Excellent |
| A- | 3.7 | |
| B+ | 3.3 | |
| B | 3.0 | Good |
| B- | 2.7 | |
| C+ | 2.3 | |
| C | 2.0 | Average |
| C- | 1.7 | |
| D+ | 1.3 | |
| D | 1.0 | Passing |
| D- | 0.7 | |
| F | 0.0 | Failing |
This grade scale is used by most institutions for calculating GPA. Note that some schools may use slightly different values, so always check your unofficial transcript or official transcript to confirm your school’s system.
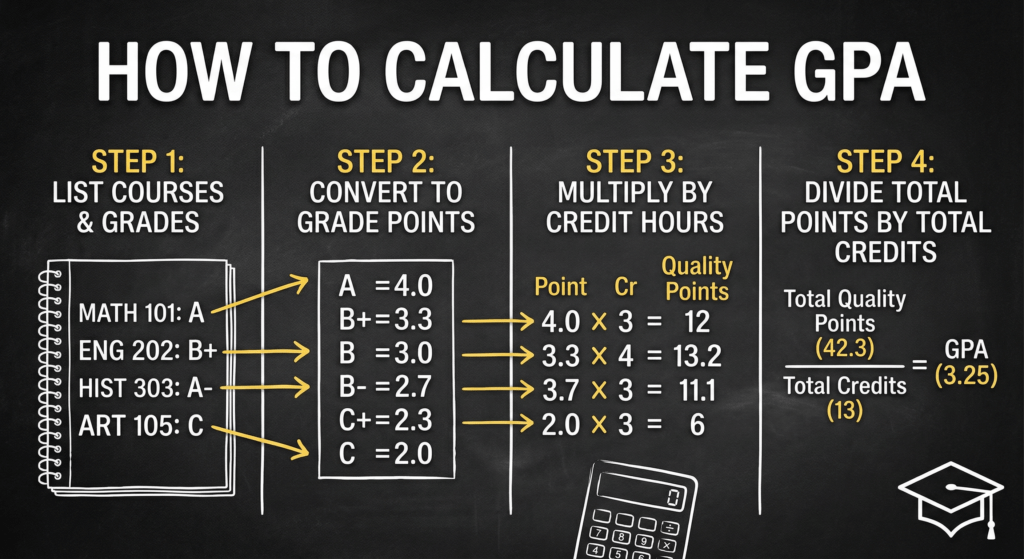
How to Calculate GPA: The Basic Formula
Calculating your GPA involves three simple steps:
GPA = Total Grade Points ÷ Total Credits
Here’s how it works:
- Convert each course grade to grade points using the scale above
- Multiply grade points by credit hours for each course (this gives you quality points)
- Add up all quality points to get total grade points
- Add up all credit hours to get total credits
- Divide total grade points by total credits
Step-by-Step GPA Calculation Example
Let’s calculate a semester GPA using a realistic example. Here’s a typical college semester:
| Course Name | Letter Grade | Grade Points | Credit Hours | Quality Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English 101 | A | 4.0 | 3 | 12.0 |
| Math 110 | B+ | 3.3 | 4 | 13.2 |
| History 150 | B | 3.0 | 3 | 9.0 |
| Biology 100 | C+ | 2.3 | 4 | 9.2 |
| PE 101 | A- | 3.7 | 1 | 3.7 |
Calculation Steps:
- Quality Points (listed in credits column): Already calculated by multiplying grade points × credit hours
- Total Grade Points: 12.0 + 13.2 + 9.0 + 9.2 + 3.7 = 47.1
- Total Credits: 3 + 4 + 3 + 4 + 1 = 15
- Semester GPA = 47.1 ÷ 15 = 3.14
Use our GPA calculator to verify your calculations and get accurate results instantly.
Calculating Cumulative GPA
Your cumulative GPA tracks academic performance across your entire high school career or undergraduate degree program. To calculate cumulative GPA, you follow the same formula but include all semesters:
Example: Calculating Overall GPA
Let’s say you completed three semesters:
- Semester 1: 3.2 GPA with 15 credit hours
- Semester 2: 3.5 GPA with 16 credit hours
- Semester 3: 3.1 GPA with 15 credit hours
Calculation:
- Find total grade points for each semester by multiplying GPA × credit hours:
- Semester 1: 3.2 × 15 = 48.0
- Semester 2: 3.5 × 16 = 56.0
- Semester 3: 3.1 × 15 = 46.5
- Add total grade points: 48.0 + 56.0 + 46.5 = 150.5
- Add total number of credits: 15 + 16 + 15 = 46
- Cumulative GPA = 150.5 ÷ 46 = 3.27
Your cumulative GPA is what appears on your official transcript and what colleges consider during the admissions process.
Unweighted GPA vs. Weighted GPA
Understanding the difference between unweighted and weighted GPA is crucial for college prep and college applications.
Unweighted GPA
An unweighted GPA uses the standard 4.0 scale for all courses, regardless of difficulty. An A in regular English and an A in AP English both equal 4.0 grade points. This is the most common calculation method and what most colleges use for college admissions decisions.
Weighted GPA
Some high schools award extra points for advanced coursework like AP classes, IB classes, or honors courses. In a weighted system:
- Regular courses: A = 4.0
- Honors courses: A = 4.5 (extra 0.5 points)
- AP/IB classes: A = 5.0 (extra 1.0 point)
This means students taking challenging courses can achieve a weighted GPA above 4.0. Use our high school GPA calculator to compute both weighted and unweighted GPAs.
Important Note: Most colleges recalculate your GPA using their own formula during the admissions process, often removing the weighted bonus to fairly compare applicants from different schools.
Special Situations in GPA Calculation
Repeated Courses
If you retake a course to improve your grade, check your school’s policy:
- Grade Replacement: Some schools use only the new grade in GPA calculation
- Grade Averaging: Others average both attempts
- Transcript Notation: Both grades usually appear on your transcript
The repeated course policy varies by institution, so verify with your registrar.
Transfer Work and Transfer Credit
When you transfer colleges, transfer credit from your previous institution may or may not count toward your new cumulative GPA:
- Credits typically transfer and count toward graduation
- Grades often don’t factor into your new school’s GPA calculation
- Your new cumulative GPA usually starts fresh
- Some graduate schools may calculate a combined GPA from all institutions
Pass/Fail Courses
Courses taken pass/fail typically don’t affect your GPA:
- Pass (P): Credit earned, no impact on GPA
- Fail (F): No credit, may count as 0.0 in some schools
- Most schools limit the number of pass/fail courses you can take
Check your academic calendar and course requirements before choosing this option.
Why Your GPA Matters
College Admissions
Your cumulative GPA is a primary factor in college applications. Admissions offices use it to evaluate:
- Academic achievement and consistency
- Readiness for college-level work
- Comparison with other applicants
Most competitive colleges look for GPAs above 3.5, while highly selective schools expect 3.8 or higher.
Graduate School
Graduate students face even higher GPA expectations. Most degree programs require:
- Minimum 3.0 GPA for admission consideration
- 3.5+ GPA for competitive programs
- Strong major GPA in your field of study
Your undergraduate performance significantly impacts graduate school opportunities.
Financial Aid Eligibility
Maintaining a minimum GPA is often required to keep financial aid:
- Federal aid typically requires 2.0 minimum
- Scholarships may require 3.0 or higher
- Loss of aid can occur if you fall below thresholds
- Some aid programs have satisfactory academic progress requirements
Job Opportunities
Many employers request GPA information for entry-level positions:
- 3.0+ is generally considered competitive
- Some companies have minimum GPA requirements
- Internship programs often require strong academic performance

Tips for Improving Your GPA
Focus on High Credit Hour Courses
Because GPA calculation weights courses by credit hours, your grade in a 4-credit course impacts your GPA more than a 1-credit course. Prioritize performance in:
- Core requirements with more total credits
- Major courses that carry significant weight
- Courses in your degree program concentration
Use Grade Calculators Strategically
Our final grade calculator helps you determine what test scores you need to achieve target grades. This strategic planning ensures you focus effort where it matters most.
Monitor Your Progress
Calculate your semester GPA after each term and track toward your goals:
- Check your unofficial transcript regularly
- Understand how each course grade affects your overall GPA
- Identify areas needing improvement early
Consider Course Load Carefully
Taking too many difficult courses simultaneously can hurt academic performance. Balance your schedule with:
- Mix of challenging and manageable courses
- Appropriate total number of credit hours
- Time for studying and coursework completion
Common GPA Calculation Mistakes
Mistake #1: Ignoring Credit Hours
Simply averaging all letter grades without considering the number of credit hours produces incorrect results. Always multiply grade points by credit hours first.
Mistake #2: Using the Wrong Grade Scale
Verify your institution’s specific grading scale. Some schools use different point values for A+, while others cap all A grades at 4.0.
Mistake #3: Including Non-Credit Courses
Ensure you only include courses that appear in the credits column of your transcript with both a letter grade and credit value.
Mistake #4: Miscalculating Transfer Credit
Understand how transfer work affects your GPA at your current institution. Don’t assume transferred courses automatically count in GPA calculation.
Using a College GPA Calculator
While manual calculation helps you understand the process, using a college GPA calculator saves time and ensures accurate results. Our GPA calculator offers:
- Automatic grade point conversion
- Weighted and unweighted GPA calculation
- Semester and cumulative GPA tracking
- “What-if” scenarios for future planning
- Mobile-friendly interface for on-the-go calculations
Simply enter your course name, letter grade, and credit hours for instant, accurate results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between semester GPA and cumulative GPA?
Semester GPA reflects one term’s coursework, while cumulative GPA averages all completed semesters throughout your academic career. Colleges focus on cumulative GPA for admissions decisions.
How do I calculate my major GPA?
Use the same formula (total grade points ÷ total credits) but include only courses that count toward your major requirements. This appears separately from your overall GPA.
Can I round my GPA on applications?
Most applications specify whether to round. Generally, you can round to two decimal places (3.45 becomes 3.5), but don’t round up full points (2.9 stays 2.9, not 3.0).
Do all courses count toward GPA?
Only courses with letter grades and credit hours count. Pass/fail courses, audit courses, and some transfer credit may not factor into GPA calculation.
How does a repeated course affect my GPA?
This depends on institutional policy. Some schools replace the old grade entirely, while others average both attempts. Check your school’s academic policies.
Tools for Academic Success
Grade Calculator – Calculate individual assignment and test scores
GPA Calculator – Track semester and cumulative GPA accurately
Final Grade Calculator – Determine what you need on finals to reach goals
Weighted Grade Calculator – Calculate grades with weighted categories
Final Thoughts
Learning how to calculate GPA empowers you to take control of your academic performance. Whether you’re tracking progress through your high school career, preparing college applications, maintaining financial aid eligibility, or pursuing graduate school, understanding GPA calculation helps you set realistic goals and monitor achievement.
Remember that while GPA is important, it’s just one aspect of your academic profile. Focus on genuine learning, consistent effort, and continuous improvement. Use the calculation methods and tools in this guide to stay informed about your academic standing and make strategic decisions about coursework.
Start tracking your GPA today with GradeCalcPro’s free calculator and take the guesswork out of grade point average calculation!